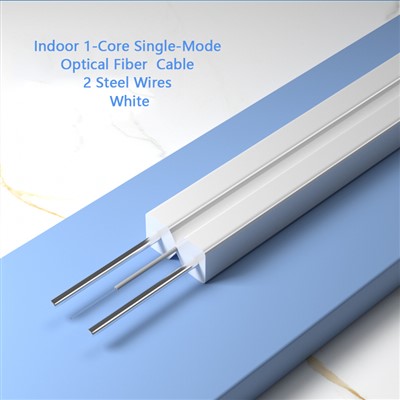
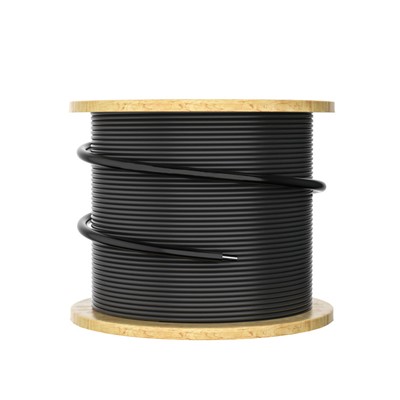
Fiber Optic Cable
Experience the future of high-speed data transmission with our state-of-the-art fiber optic cable. Designed for unparalleled performance, our cable offers a seamless and reliable connection that is essential for modern communication systems.
Key Features:
High Bandwidth: Capable of transmitting large amounts of data at the speed of light, ensuring that you stay ahead in the fast-paced digital world.
Low Attenuation: With minimal signal loss over long distances, our cable maintains the integrity of your data from source to destination.
Durability: Constructed with the highest quality materials, our cable is built to withstand harsh environments and provide long-lasting service.
Flexibility: The lightweight and flexible design makes installation easy and adaptable to various routing requirements.
What Is Fiber Optic Cable
Fiber optic cable is a type of cable that contains one or more thin strands of glass or plastic fiber that transmit data using light waves. The fiber strands are encased in a protective sheath and are able to carry large amounts of data at high speeds over long distances. Fiber optic cable is commonly used in telecommunications networks, internet infrastructure, and other data transmission applications. It is known for its reliability, speed, and security as it is difficult to intercept or tap into fiber optic signals.
Advantages of Fiber Optic Cable
High Bandwidth: Fiber optic cables offer higher bandwidth than traditional copper cables. This means that they can carry more data over longer distances without losing signal quality.
Faster Speeds: Because of the high bandwidth capabilities of fiber optic cables, data can be transmitted at faster speeds. This makes them ideal for high-speed internet and network connections.
Immunity To Electromagnetic Interference: Fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference, which can cause signal degradation and data loss with traditional copper cables.
Longer Transmission Distance: Fiber optic cables can transmit data over much longer distances than traditional copper cables, without losing signal quality. This is especially important for applications like telecommunications and undersea cables.
Durability: Fiber optic cables are much more durable than traditional copper cables. They are resistant to physical damage, weather, and temperature fluctuations.
Security: Fiber optic cables offer a higher level of security than traditional copper cables. They are much more difficult to tap into or intercept, making them ideal for sensitive data transmissions.
Reliability: Fiber optic cables are immune to environmental factors such as lightning, electrical interference, and temperature changes, which makes them highly reliable and consistent.
Lower Latency: Because of the faster speeds and higher bandwidth capabilities, fiber optic cables can reduce latency and improve performance in high-demand applications like online gaming and streaming video.
-
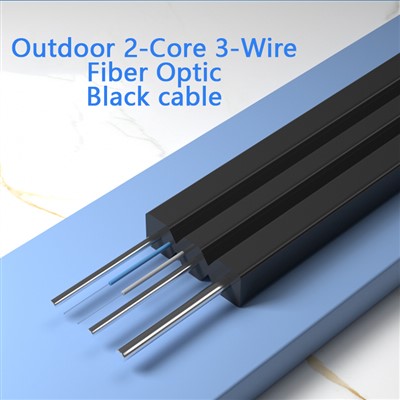
1000M Single Mode Fiber OpticProduct Features: The Outdoor Single-Mode 2-Core 3-Wire Fiber Optic Cable is designed for robust andread more
-
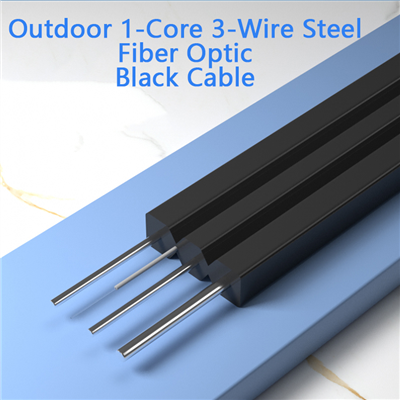
Outdoor Single-Mode Covered Fiber Single-Core 3-Wire Optical Cable BlackProduct SpecificationsBrand: HKS-CableCore Type: 1-core outdoorMaterial: Thick phosphated steel wireread more
-
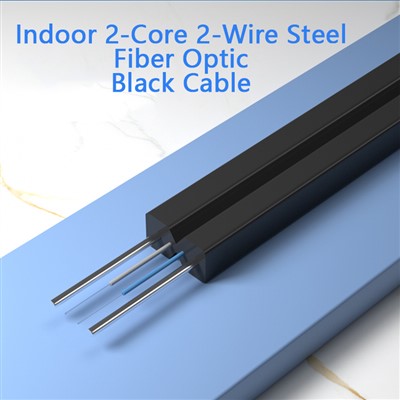
Black Indoor 2 Core 2 Wire Steel Fiber Optic CableEmbark on a journey through the veins of modern communication with HKS-Cable's latest innovaread more
-
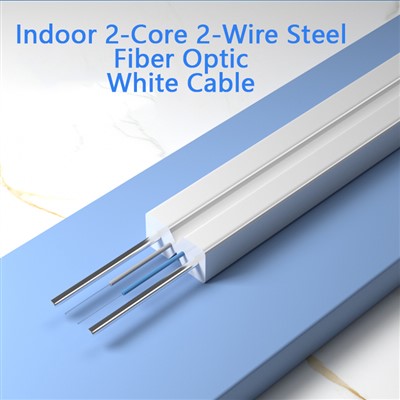
Indoor 2-Core 2-Wire Steel Fiber Optic White CableIn the ever-evolving world of data transmission, HKS-Cable stands at the forefront, introducing theread more
-
Black Single Mode Optical Fiber CableProduct Features: The Black Single Mode Optical Fiber Cable by HKS-Cable is a single-core fiber desiread more
-
Indoor Optical Fiber Network CableProduct Introduction - Indoor Optical Fiber CableIntroducing our Indoor Optical Fiber Network Cable,read more
-
Fiber Optic Cable Single-Mode 2-288coreProducts FeaturesPremium Core Material: G657A2 fiber cores deliver exceptional signal transmission qread more
Why choose us
We are looking for a cooperative partner to expand our business.
Rich Experience
Our company has many years of production work experience. The concept of customer-oriented and win-win cooperation makes the company more mature and stronger.
One-stop Solution
With rich experience and one-to-one service,we can help you choose products and answer technical questions.
Quality Control
We have professional personnel to monitor the production process, inspect the products and ensure that the final product meets the required quality level standards, guidelines and specifications.
Advanced Equipment
Equipment based on the latest technological developments has higher efficiency, better performance and stronger reliability.
Competitive Price
We have professional sourcing team and cost accounting team, stive to reduce cost and profit and provide you a good price.
After-Sale Service
Professional and thoughtful after -sales team, let you worry about us after -sales Intimate service, strong after -sales team support.
How Fiber Optic Cables Work
A fiber optic cable consists of one or more strands of glass, each only slightly thicker than a human hair. The center of each strand is called the core, which provides the pathway for light to travel. The core is surrounded by a layer of glass called cladding that reflects light inward to avoid loss of signal and allow the light to pass through bends in the cable.
The two primary types of optical fiber cables are single mode and multi-mode. Single-mode fiber uses extremely thin glass strands and a laser to generate light, while multi-mode optical fiber cables use LEDs.
Single-mode optical fiber networks often use Wave Division Multiplexing techniques to increase the amount of data traffic that the strand can carry. WDM allows light at multiple different wavelengths to be combined (multiplexed) and later separated (de-multiplexed), effectively transmitting multiple communication streams through a single light pulse.

As noted above, fibre optic cables are constructed from numerous materials and components - but the core strands themselves are usually made from some combination of glass (silica) and/or plastic.
Plastic optical fibres tend to be more economical and easier to work with due to their increased flexibility, lighter weight and resistance to bending and shock. They’re generally used for applications where lower transmission rates and speeds are acceptable, and where the risk of mechanical stress is lower - such as in lower-speed, shorter-distance runs as part of home, industrial or automotive networks.
Optic cables are commonly found in a variety of applications such as the internet and broadband, phone lines, networking, and telecommunications. Additional fibre optic cable uses in the home and workplace include lighting and interior decor.
Optical fibre cable can save space compared to bulkier traditional cabling. This ability has also made it popular for many safety and lighting features in vehicles. Optical fibre technologies are widely used in many other demanding professional fields too, including in medical applications, for detailed mechanical inspections, and as sensors for monitoring and controlling the flow of various sorts of electrical currents, sounds and chemicals.
Optical Fibre Internet And Networking
Fibre optic internet cable is increasingly popular. This is due to the higher speeds and bandwidth it can provide compared to standard ethernet or Wi-Fi signals delivered via coaxial or even copper wire from street-level exchanges. This means that fibre networking is a far better choice where high speeds are advantageous or for particularly intensive data transfer needs. Much of this is also true for fibre optic phone lines.
Fibre optic bandwidth is usually significantly higher than a typical ethernet connection. Fibre is also safe to use in high-voltage locations, and in areas where flammable gases or other harsh chemicals or weather conditions are likely to be a factor. This can be another important factor in choosing fibre optic cables for broadband delivery and telecoms as opposed to standard ethernet.
Fibre Optic Cables For Lighting
LED lighting is also a common application of fibre optic technology in domestic and commercial environments. Fibre optics can transmit data in a clean and versatile manner across a wide spectrum of colours and patterns. This means that it is widely used in decorative lighting applications, accent lights, and feature lamps.
Far less electricity is also used by fibre optic LED lighting compared to standard bulb options, which makes it both environmentally friendly and economical. You can buy fibre optic lighting cables that are safe to use in a wide variety of applications and environments. They do not carry electrical current and are largely resistant to general wear, damage and degradation.
How Do Fibre Optic Cables Work
In understanding how data is sent through fibre optic cables, it’s important to note that there are multiple components involved in the construction of an optical fibre that are all required to ensure they work properly. Obviously, the glass strands themselves are absolutely central to the system working at all - but there are also a number of other key parts that all play a role in successful data transfer along optical fibres.
Firstly, there needs to be a source of light to send information ‘pulses’ along the strands of transparent glass or plastic tubing at the core of the cable. This is usually created either by a tiny laser or by an LED source, which receives an input signal coming from transmitter circuitry and converts it to a light pulse before bouncing it along the fibre cores.
Secondly, it’s key that the glass fibres themselves are surrounded by an additional glass or plastic cladding layer, which will have a different refractive index for light passing through it than the core strands. These refractive differences between the cladding and the glass fibres it surrounds are what allow the incoming light pulses to be bent at particular angles as it travels the length of the cable.
The light pulses are confined within the transparent parts of the fibre cable thanks to its internal reflective properties, moving in a zig-zagging pattern to pass around bends as they travel along the full run length of the fibre optics. In order to retain sufficient signal strength throughout particularly long cable runs, they may need to be converted to an electrical signal and back to a light pulse again at various points along the way. This is done by additional internal components known as repeaters.
When the light signals eventually reach their intended destination - having been travelling at around 70% the speed of light for most of the way - they can finally be interpreted as data or communication signals and converted to an output by the receiving equipment.
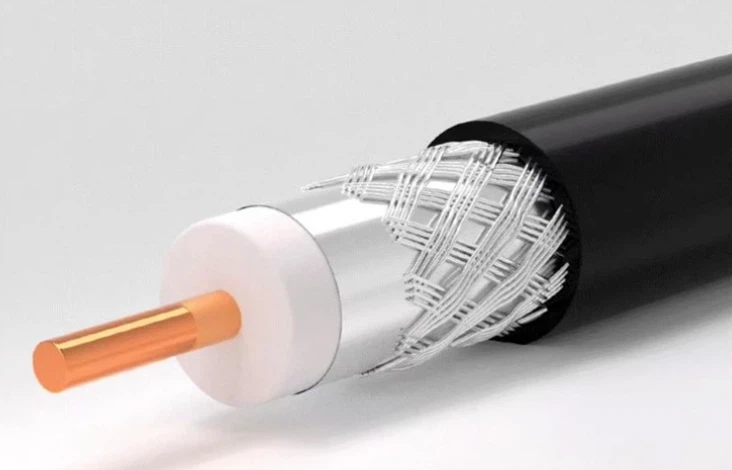

Advantages of Fiber Optic Cables Over Copper Cables
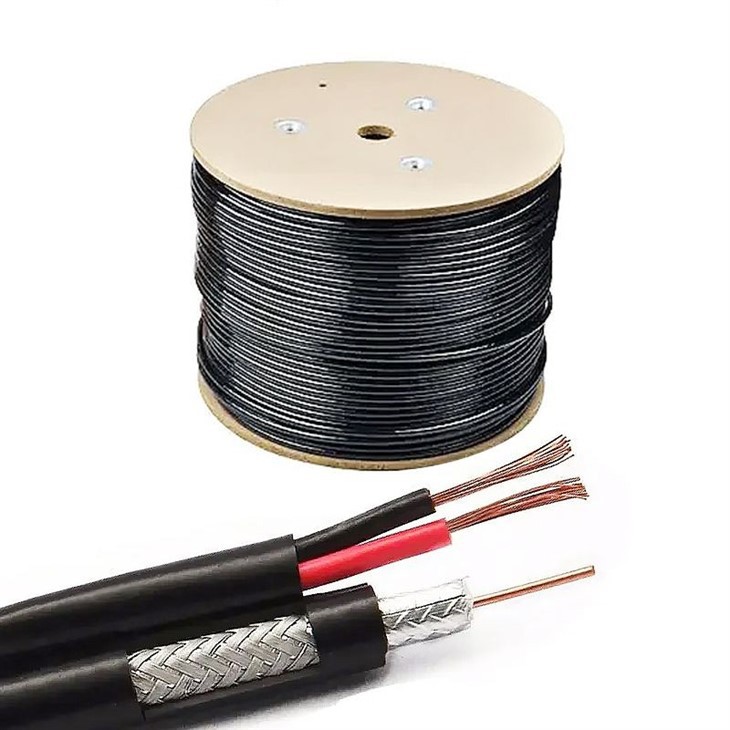
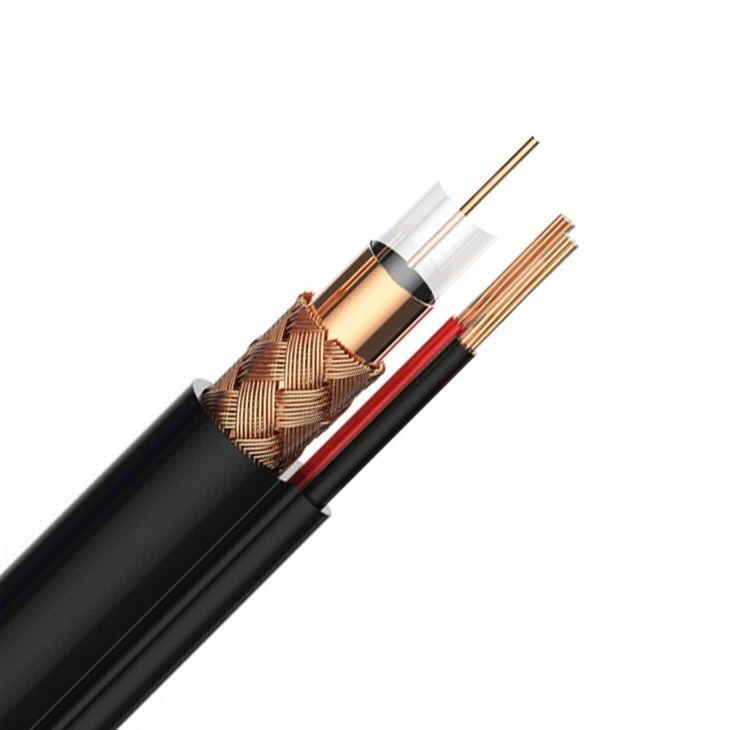




Greater Bandwidth
Copper cables were originally designed for voice transmission and have a limited bandwidth. Fiber optic cables provide more bandwidth for carrying more data than copper cables of the same diameter. Within the fiber cable family, singlemode fiber delivers up to twice the throughput of multimode fiber.
Faster Speeds
Fiber optic cables have a core that carries light to transmit data. This allows fiber optic cables to carry signals at speeds that are only about 31 percent slower than the speed of light—faster than Cat5 or Cat6 copper cables. There is also less signal degradation with fiber cables.
Longer Distances
Fiber optic cables can carry signals much farther than the typical 328-foot limitation for copper cables. For example, some 10 Gbps singlemode fiber cables can carry signals almost 25 miles. The actual distance depends on the type of cable, the wavelength and the network.
Better Reliability
Fiber is immune to temperature changes, severe weather and moisture, all of which can hamper the connectivity of copper cable. Plus, fiber does not carry electric current, so it’s not bothered by electromagnetic interference (EMI) that can interrupt data transmission. It also does not present a fire hazard like old or worn copper cables can.
Thinner and Sturdier
Compared to copper cables, fiber optic cables are thinner and lighter in weight. Fiber can withstand more pull pressure than copper and is less prone to damage and breakage.
More Flexibility for the Future
Media converters make it possible to incorporate fiber into existing networks. The converters extend UTP Ethernet connections over fiber optic cable. Modular patch panel solutions integrate equipment with 10 Gb, 40 Gb and 100/120 Gb speeds to meet current needs and provide flexibility for future needs. The panels in these solutions accommodate a variety of cassettes for different types of fiber patch cables.
Lower Total Cost of Ownership
Although some fiber optic cables may have a higher initial cost than copper, the durability and reliability of fiber can make the total cost of ownership (TCO) lower. And, costs continue to decrease for fiber optic cables and related components as technology advances.
Difference Between Multimode And Singlemode Fibre Optic Cable

Based on product type, the market can be divided into single-mode fiber and multi-mode fiber. Single mode optical fibre allows one type of light mode to be propagated at a time. However, multi-mode fiber cable can propagate multiple modes. Multi-mode optical fiber can be used for short-distance runs, while single mode fiber cable can be used for long-distance applications. Hence, the mode fiber segment is expected to grow much faster during the forecast period owing to their long-distance applications and low installation costs as compared to multi-mode fiber.

Single mode fiber optic cable‘s core diameter (9 µm) is much smaller than multimode fiber (50 µm and 62.5 µm). Its typical core diameter is 9 µm. This enables the multimode fiber to have a higher “light-gathering” ability and simplify connections. The cladding diameter of single mode and multimode fiber is 125 µm.
types of CNC machining
For fiber optic cables to replace the copper cables, they must safely be applied and maintained in all the application and environments where metallic conductor cables are installed and maintained. Due to its fragile structure, Fiber cables must be protected and must have very good mechanical properties to work in these environments such as underground ducts, direct burial or Aerial Application.
However, glass optical fibers themselves are very fragile and very susceptible to mechanical handling and strike.That’s why, the optical fiber glass fibers are wrapped by protective materials including coating and cabling to be able to handle the mechanical impacts and strikes in installation and maintenance.
Due to above mentioned facts, fiber optic cables are designed and based on four characteristics.
●BUFFER (Optical Fiber)
In a fiber optic cable, a buffer is one type of component used to encapsulate one or more optical fibers for the purpose of providing such functions as mechanical isolation, protection from physical damage and fiber identification.
Bare glass fibers are composed of core and cladding and both are based on silica or other glass materials.
The buffer may take the form of a miniature conduit, contained within the cable and called a "loose buffer(Loose Tube)", or "Tight Buffer”. A loose or tight buffer may contain more than one fiber, and sometimes contains a lubricating (thixotropic) gel. A "tight buffer" consists of a polymer coating in intimate contact with the primary coating applied to the fiber during production
Loose Tube: Loose tube fibers are designed for harsh environmental conditions in the outdoors. In loose tube cables, the coated fiber “floats” within a rugged, abrasion resistant, oversized tube which is filled with optical gel.
Tight Buffer: Tight buffered cables, in contrast, are optimized for indoor applications. In the tight buffer construction, instead of using the gel layer loose tube cable has, it uses a two-layer coating.
●Strength Members
A strength Member is an added component to a jacketed Cable to help protect and strengthen the cable construction. Most of the time it is Aramid Yarn and Glass Yarn, but can also be a flexible, but stiff fiberglass rod that runs the length of the cable. That part of a Fiber Optic Cable composed of aramid yarn, steel strands, or fiberglass filaments that increase the Tensile Strength of the cable.
Structural and strength members can be solid or stranded steel wire, Aramid Yarn or fiber glass. They must have a high Young’s modulus, high strain capability, flexibility and low weight per unit length.
●Fiber Cable Jacket
The fiber optic cable cab be surrounded by an outer jacket for reducing the abrasion and the first line of defense against the surrounding environment. This layer of the cable is usually made of plastic based products and called fiber cable jacket or fiber cable sheath. It resists water entry while remaining inert to gases and liquids that the cable may be exposed to during its service life
The fiber cable jacket contains the cable core and has various complexity from one simple extruded plastic jacket to a multilayer structure consisting of two or more jackets and with intermediate armoring.
Types
PE - Polyethylene (MDPE - medium density PE / HDPE - high density PE)
•Primary outside jacket material.
•Good resistance to UV (sun light) due to carbon black.
•Good flexibility over wide range of temperatures.
•Good abrasion and crack resistance.
PVC -Polyvinyl chloride
•Provides good mechanical protection.
•Flexible at normal installation temperatures.
•Flame retardant.(typical riser material)
•Used for many indoor applications.
•Can be protected against sunlight with various UV inhibitors.
LSZH - Low smoke, zero halogen
•Flame Retardant with low smoke and no halogenated materials
•For use in unventilated areas exposed to public, e.g., subways and tunnels.
•Good mechanical performance.
●Water/Flooding Barrier
Fibre optic cables are usually installed in non-watertight piping and cable ducts. The fibres need to be effectively protected from humidity and water flooding in order to make sure the operational reliability of the fiber optic cables.
And the plastic sheath material tends to give very limited protection against the penetration of water into the cable.
General water barriers for regular cables are axially laid aluminum foil/polyethylene laminated film immediately inside the polyurethane or polyethylene plastic sheaths; and/or the use of moisture resistant compounds such as Swallable Glass Yarn around the fibers.
Certifications






Our Factory
Shenzhen Haikang Plastic Wire and Cable Co., Ltd. is a comprehensive trading company specializing in the production and processing of copper core cables and wires. The company has advanced production equipment, a strong technical team, and complete testing methods. With strong technical expertise, first-class equipment and perfect management system, it takes a leading position in innovative cable design and manufacturing. The company has its own factory in Chigang Town, Jieyang City, Guangdong Province, China, with a fifteen-year development history and rich production experience.

FAQ