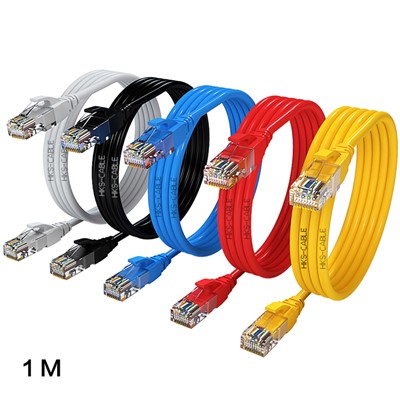
Patch Cord
What Is Patch Cord
A patch cord is a short electrical cable that is used to connect two electronic devices or components. It is typically used in networking and telecommunications to connect devices such as computers, routers, switches, and patch panels. Patch cords are designed to be flexible and easy to use, and they generally have connectors on both ends that can be plugged into a port. They may also be known as patch cables, Ethernet cables, or jumper cables.
Advantages of Patch Cord
Flexibility: Patch cords can be easily moved or rearranged to fit changing network requirements. This flexibility allows for easier maintenance and expansion of the network.
Durability: Patch cord cables are designed to withstand heavy usage, damage, and wear and tear. They are typically made of high-quality materials that ensure long-lasting performance.
Ease Of Installation: Patch cord cables with pre-terminated connectors, make installation quick and easy, and can be utilized with different lengths to connect devices that are at different distances.
Versatility: Patch cords come in a variety of lengths and types, and can be used to connect various types of devices together. They work with a wide range of networking equipment like switches, routers, servers, and patch panels.
Reliable Connection: A patch cord forms a direct and uninterrupted physical connection between two devices, resulting in a stable and reliable network connection.
Customizability: Patch cords come in a variety of lengths, colors, and connector types, making them highly customizable to meet the specific needs of an individual or organization.
-
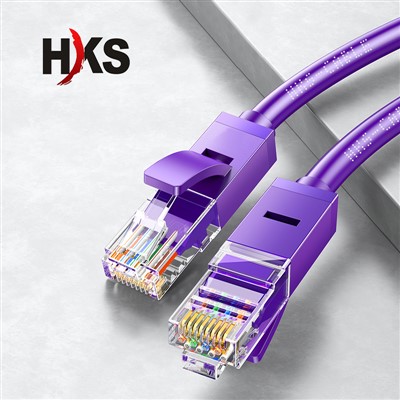
Purple Cat5e Jumper CableProduct Features:Our Cat5e Purple Network Cable boasts pure copper conductors and a durable PVC jackread more
-
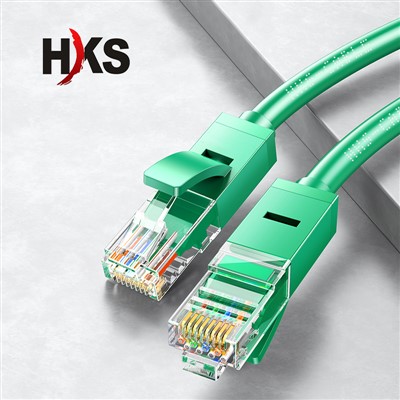
Green Cat5e Cable RJ45Product Features: The Green Cat5e Patch RJ45 Cable offers high-speed transmission up to 1 Gbps and sread more
-
Cat5e Cable 100MProduct Features:Designed for high-performance network connections, the Cat5e Cable 100M features hiread more
-
cat5e 50m cableCat5e 50m Cable Features:The Cat5e 50m Cable is a high-quality Ethernet cable designed to meet moderread more
-
30m cat5e cableProduct Features:The 30m Cat5e cable is a high-performance Ethernet cable that meets ANSI/TIA-568-D.read more
-
20m Cat5e Patch CableHigh-quality, machine-made network cable with 8 fully connected cores, compatible with 10Mbps, 100Mbread more
-
10M Cat5e Patch CableProduct FeaturesOur 10M Cat5e Patch Cable offers data transfer speeds of up to 1Gbps, ensuring stablread more
-
5m Cat5e Patch CableThe A 5m Cat5e Patch Cable is designed to provide reliable and high-speed Ethernet connectivity. Itread more
-
3m cat5e patch cableProduct FeaturesThe 3m Cat5e patch cable is a high-performance network cable suitable for 10Mbps, 10read more
-
2m cat5e patch cableProduct Features: The Cat5e 2m Patch Cable supports data speeds up to 1000Mbps. It features pure copread more
-
Patch Cable Cat5e 1.5mProduct Features:The Patch Cable Cat5e 1.5m is designed for high-speed data transmission, supportingread more
-
Cat5e UTP Cable 1mProduct Features:The Cat5e UTP Cable (1m) is designed for optimal network connections, featuring higread more
Why choose us
Rich Experience
Our company has many years of production work experience. The concept of customer-oriented and win-win cooperation makes the company more mature and stronger.
One-stop Solution
With rich experience and one-to-one service,we can help you choose products and answer technical questions.
Quality Control
We have professional personnel to monitor the production process, inspect the products and ensure that the final product meets the required quality level standards, guidelines and specifications.
Advanced Equipment
Equipment based on the latest technological developments has higher efficiency, better performance and stronger reliability.
After-Sale Service
Professional and thoughtful after -sales team, let you worry about us after -sales Intimate service, strong after -sales team support.
Competitive Price
We have professional sourcing team and cost accounting team, stive to reduce cost and profit and provide you a good price.
How Many Types Of Patch Cords Are There
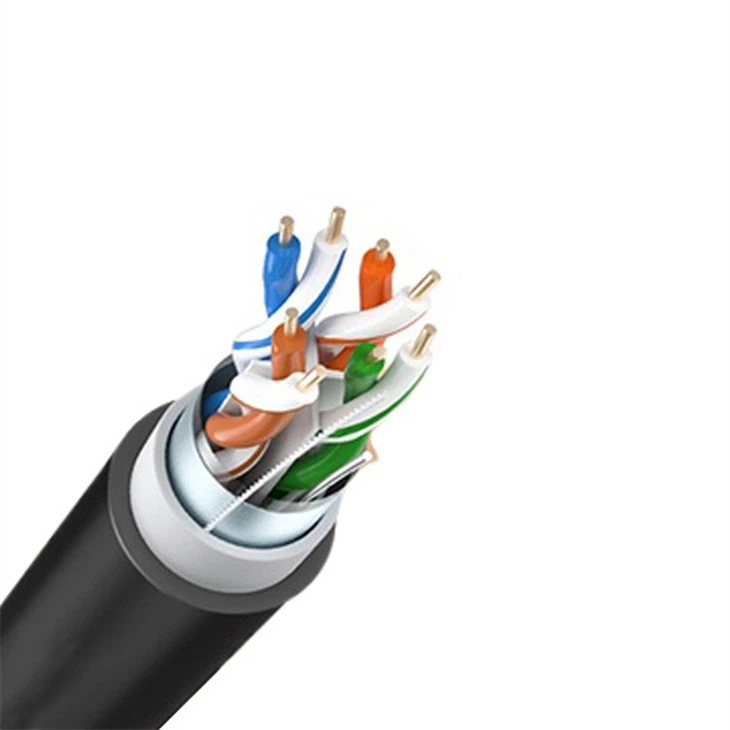




There are several types of patch cords; mainly there are two types of patch cords
UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) and
STP (Shielded Twisted Pair).
UTP patch cords can be classified into three categories: Straight-through, Crossover, and Rollover.
STP patch cords can be classified into straight-through and Crossover.
Let us know more about the types of patch cords here
OFC Patch Cord
OFC Patch Cord is a multimode or single-mode fiber optic cable restrained at either end with connectors that allow it to be rapidly and conveniently conjoined to CATV, an optical switch, or other telecommunication equipment. Its thick layer of security helps connect the optical transmitter, receiver, and terminal box.
LC-LC Patch Cord
L.C. patch cord is an essential component for data center and network deployment, and it provides the necessary connectivity between fiber optic equipment. L.C. cable assembly offers a simple solution for installing and maintaining fiber optic cables in high-density applications. It is easy to change or rearrange your cabling with an L.C. patch cord without reconfiguring the entire system. The ends of an L.C. fiber optic patch cord are identical in appearance, and the orientation of the cable can only differentiate it.
S.C. to L.C. Patch Cord
A Standard-Cable (S.C.) to a Low-Profile-Cable (LPC) is a conversion from a larger type of connector to a smaller one that connects devices with a small form factor connector (S.C.) to devices with a larger form factor connector (L.C.). It is useful in connecting any device with a single-mode fiber optic connector to a multimode connection. he SC connector is typically beneficial on the transmitting end of the line during the L.C. connector on the receiving end.
Optical Fiber Patch Cord
An optical fiber patch cord is a valuable cable connecting two optical fibers. It is typically made up of a connector on each end, and a flexible or rigid sleeve, which protects the connectors and helps the cable jacket stays in place. It is a small, rugged optical link connector that provides high-bandwidth transmission over a short distance. Optical fiber patch cords are one of the most critical components in an optical network. It helps connect an optical network terminal to a fiber splice closure or an optical distribution frame.
S.C. to F.C. Patch Cord
An SC to F.C patch cord is a cable with a connector on one end and a connector on the other end. The connectors are specifically designed for fiber optic cables. These cables provide connectivity between a transceiver and a fiber optic device. They consist of a thin plastic jacket over a single glass or plastic fiber core. The connectors at each cable end usually have molded boots and thumbscrews for protection. They can also connect two transceivers. These cables have compatibility with single-mode and multimode specifications by having an S.C. connector at one end and F.C. connectors (S.C., S.T., L.C.) at the other end.
Single-Mode Fiber Patch Cord
A single-mode fiber patch cord refers to a fiber optic cable with two ends helpful for optical networking. It has a high-speed transmission medium compared to multimode and low attenuation. It is often beneficial in network hardware like switches, routers, and fiber optic cables. It is most commonly helpful in Ethernet network architecture, and it is also referred to as an Ethernet cable.
Multimode Patch Cord
A multimode patch cord (also known as multimode or MM fiber) is a fiber optic cable that can connect a single device to another device or multiple devices. It is a patch cord with two or more connectors at both ends. Two connectors are used to create a duplex connection, and more than two connectors are used to develop multiport relationships in the network.Multimode fiber optic cabling applications commonly connect a computer network interface card or a multiplexer/demultiplexer to a fiber optic backbone or communications cable.
Patch Cord CAT6
CAT6 Patch Cable is a high-quality network cable used to connect computer equipment. It usually has eight wires surrounded by an outer covering for protection and insulation. The eight wires consist of 4 twisted pairs of 24 gauge wire, each color-coded. These are usually helpful in connecting an Ethernet switch or hub to a computer, server, or other networking equipment.
D-Link Patch Cord
The D-Link Patch Cord is a twisted stranded cable terminated with modular plugs at both ends. These cables include two pairs of wires: one for transmitting data and the other for receiving data. Each twisted pair is usually wrapped in foil. The foil shields the wires from outside interference, thus reducing noise. This patch cord is appropriate for high-speed data transmission.
SC-LC Patch Cord
An SC patch cord is a short cable used to connect different networking devices. SC-LC patch cord is a type of twisted-pair cable commonly valuable for 10/100/1000BaSE-T networks for connecting network interface devices to the hub or switch.It has two connectors, which are usually more significant than the other. The smaller connector connects to one device while the larger connector connects to another device.
What Are The Differences Between Patch Cords And Ethernet Cables
While the two are similar, there are differences. Patch cords are commonly used to connect traditional devices such as telephones and audio/video equipment to power sources. But they can also be used as Ethernet cables which are typically used to connect devices within a local area network, like PCs, routers and switches.
By definition, Ethernet is a protocol standard that defines the way that bits of information travel over a particular medium. The two most common Ethernet cables are traditional copper cables and fiber-optic cables. The twisted pair or coaxial cable and category cable (Cat5, Cat5e and Cat6) also belong to the Ethernet cable family.
“An Ethernet cable resembles a phone cable but is larger and has more wires,” explains Bradley Mitchell on Lifewire.com, “Both cables share a similar shape and plug, but an Ethernet cable has eight wires and a larger plug than the four wires found in phone cables. Ethernet cables plug into Ethernet ports, which are larger than phone cable ports. An Ethernet port on a computer is accessible through the Ethernet card on the motherboard.”
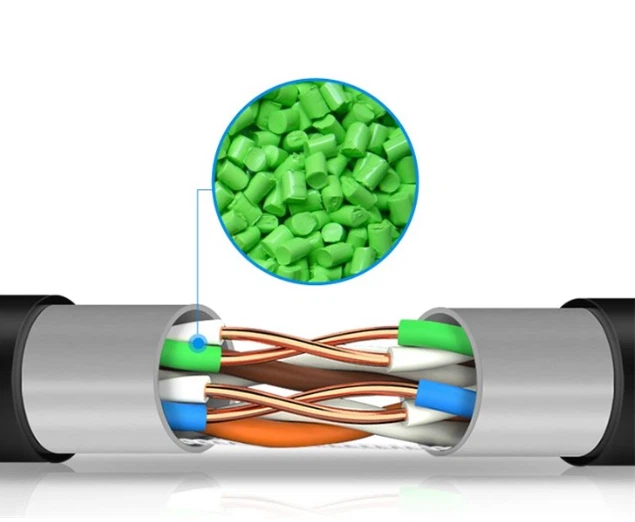
However, main differences between the two also include their lengths and their purposes. Ethernet connections are generally designed for speed and long distances. These are often called the “backbone” or “long haul” in the world of cabling.
“Similar with Ethernet cables, there are fiber patch cable and Ethernet patch cable, like LC fiber patch cable or Cat6 RJ45 patch cable,” informs Chloe Wang of Fiber Optic Solutions, “And patch cables are often used for short distances in offices and wiring closets. Ethernet patch cable can link a computer to a network hub, router or Ethernet switch, which is useful for constructing home computer networks.”
Tips On Selecting The Right Patch Cords
Patch cords are very common, and often mistakenly thought of as commodity items. However, the technical features of a patch cord play a significant role in the transmission of data signals. This is especially important in mission-critical applications
Definition Of A Patch Cord
A patch cord is a predefined length of cable with a connector at each end. It’s used to connect one network device to another network device. For example, to connect a switch port or a server to the structured cabling system.
A patch cord can utilize a copper cable that has a RJ45, TERA, or GG45 connector on both ends. Note, however, that there are hybrid versions that have different types of connectors on the ends. Copper patch cords can be shielded or unshielded, as the conditions for their use require.
Fiber optic patch cords are typically called fiber jumpers, and are either standard jumpers or mode conditioning jumpers.
Common Uses Of Patch Cord
One of the most popular uses of patch cords is to connect a laptop, desktop computer, or other end device to a wall outlet.
In a Data Center, patch cords are used to hook up equipment in one rack or enclosure to equipment on another shelf of the same rack, or to equipment on a different rack or enclosure. Their use is ubiquitous in a data center, and critical to optimizing the performance of the equipment and the network.
In computer networks, patch cords are also heavily used in telco closets, often located on each floor of a commercial building.
In telecommunications applications, patch cords are used to connect switches in Central Offices, co-location centers, and even for making OSP (outside plant) connections.
Patch Cord Design
There are two factors to be concerned with when selecting a patch cord
●Performance Characteristics of Patch Cord Fiber
Be sure to specify a cable and connector design that will optimize the signal transmission in the application for which it will be used. If there is a lot of “noise” (EMI/RFI) in the environment, you may need to use a shielded copper cable. A quality assembly operation, one with expert engineering capabilities, can help you design the exact type of shielding you need.
Stringent testing during the various steps in the assembly process can assure fiber optic patch cord performance. These tests should cover
Insertion/Return Loss (IL/RL)
Attenuation
Geometry (Including Concentricity And Light Continuity)
An End Face Inspection After Polishing The Fiber Ends
●Physical Characteristics Patch Cord Fiber
The physical construction of the cable and connector must be able to withstand the conditions and stresses of the environment, such as
Excessive Heat Or Cold
Moisture And Humidity
Foot Traffic
Production Scrap Material
Oil And Other Fluids
Both physical and performance characteristics are important and can affect each other. As such, they can also create a trade-off situation where you need to arrive at a compromise to balance the design and optimize performance of the patch cord. A reliable assembly manufacturer with strong engineering capabilities can assist you in arriving at the optimal design for your application.
Testing Patch Cords
All cabling channels in a structured cabling system are tested. It is called a “channel test” if patch cords are included; a “permanent link test” otherwise. Patch cord testing requires special connectors. Patch cords should not be tested using other test methods.
Many manufacturers who perform the required testing on EIA/TIA Category cables or patch cords, which will eventually be installed in a structured cabling system, may meet or exceed the required performance parameters in the factory. However, once the patch cords are installed in the field, the excessive handling can damage the patch cord and affect its performance to a point where it does not pass the field test requirements. Therefore, selecting a good quality assembly operation with a strict Quality Management System is imperative to obtaining quality patch cords that will maintain the factory tested performance characteristics when tested again in the field.
Patch Cable vs Crossover Cable, What’s the Difference
Wiring Configuration
As we mentioned above, the main difference between patch cables and crossover cables is that they are wired differently, with patch cables being in a straight-through configuration with the same connectors at both ends. In contrast, crossover cable wiring are crossed configurations, catering to the direct connection of network devices.
Device Compatibility
Patch cables and crossover cables are also very different when considering device compatibility. This is due to the fact that they make connections between different devices. This includes computers, switches, routers, and servers. Patch cables ensure seamless communication by connecting the transmitting signal on one device to the receiving signal on another, and this wiring solution has a high level of compatibility. In contrast, crossover cables have a crossover wiring configuration that makes them suitable for direct connections between similar devices. They are typically used when directly connecting two computers or two switches. Due to their crossed-wiring configuration, crossover cables are often incompatible with devices that require a standard straight-through connection.
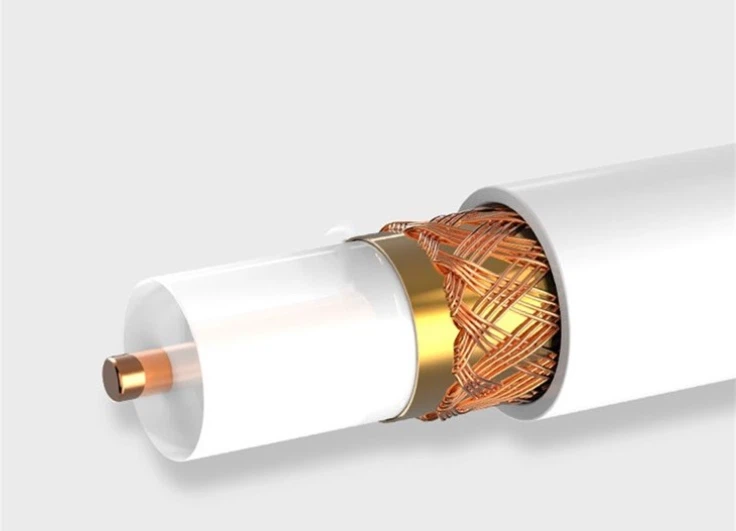
How to maintain Patch Cord
Keep It Clean
Regularly clean your patch cords with a dry cloth or an anti-static wipe to remove any dust or debris that may have accumulated on them.
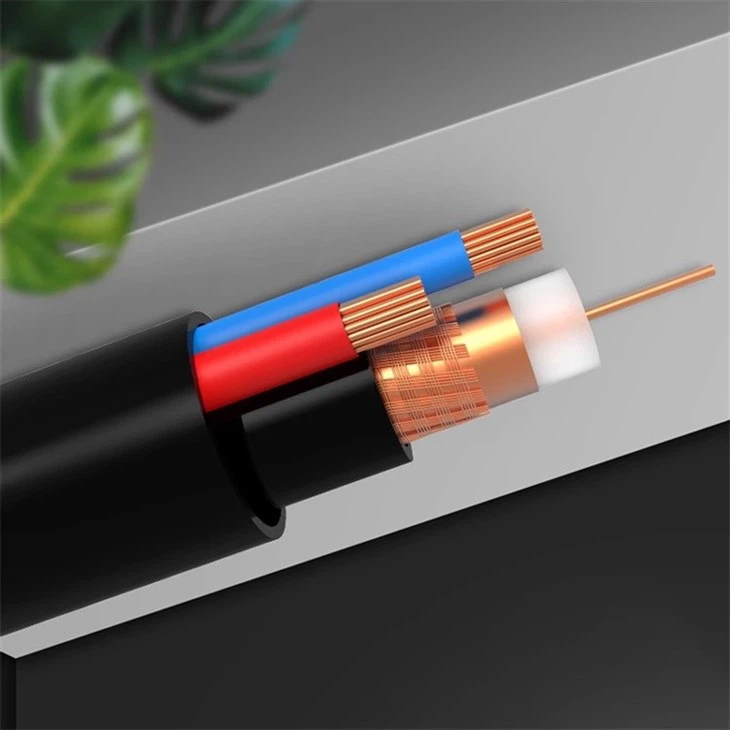
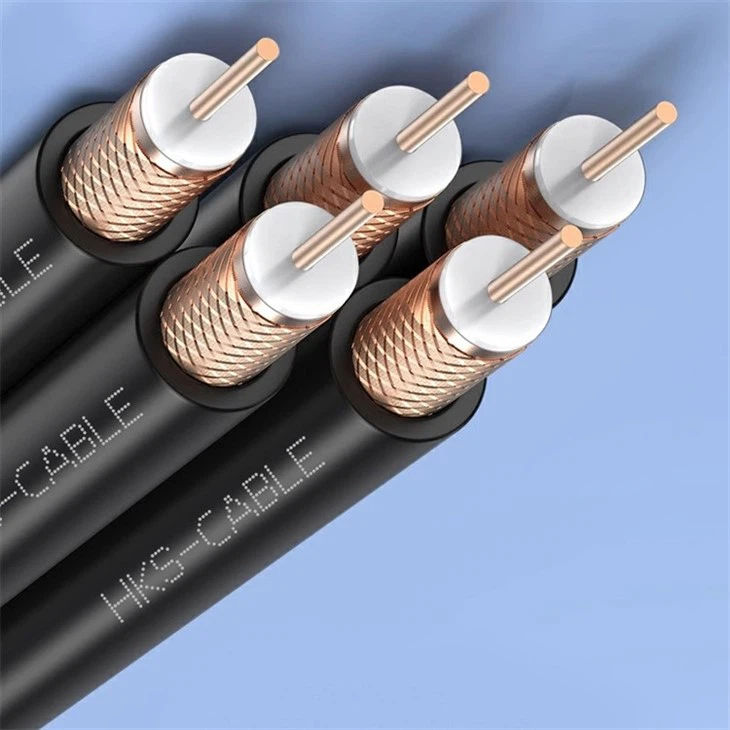


Avoid bending
Do not bend the patch cord at an angle that exceeds its minimum bend radius as this can lead to damage to the cord and affect its performance.
Store Properly
When you are not using the patch cords, store them properly in a cool, dry and dust-free environment. You can coil the cords and secure them with ties or Velcro fasteners to prevent tangling.
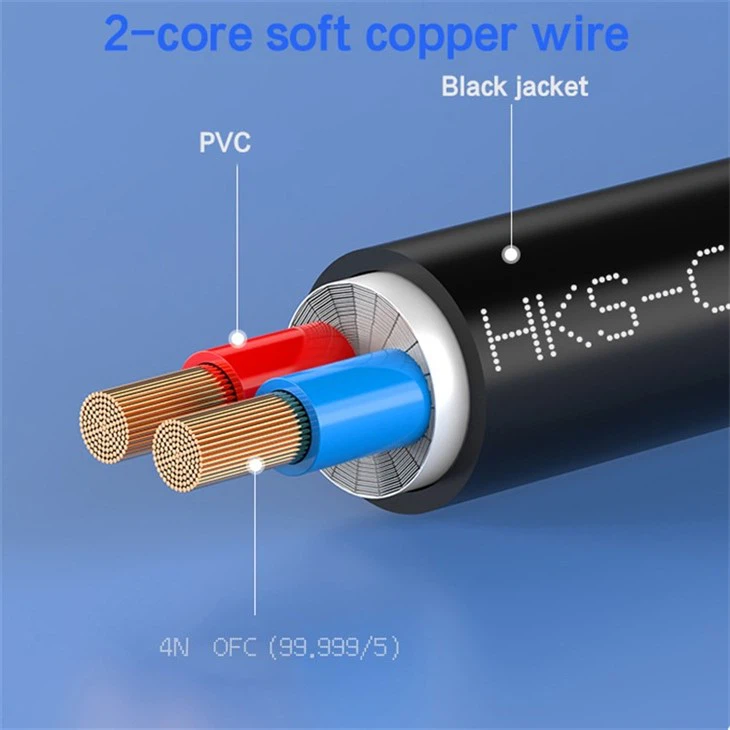
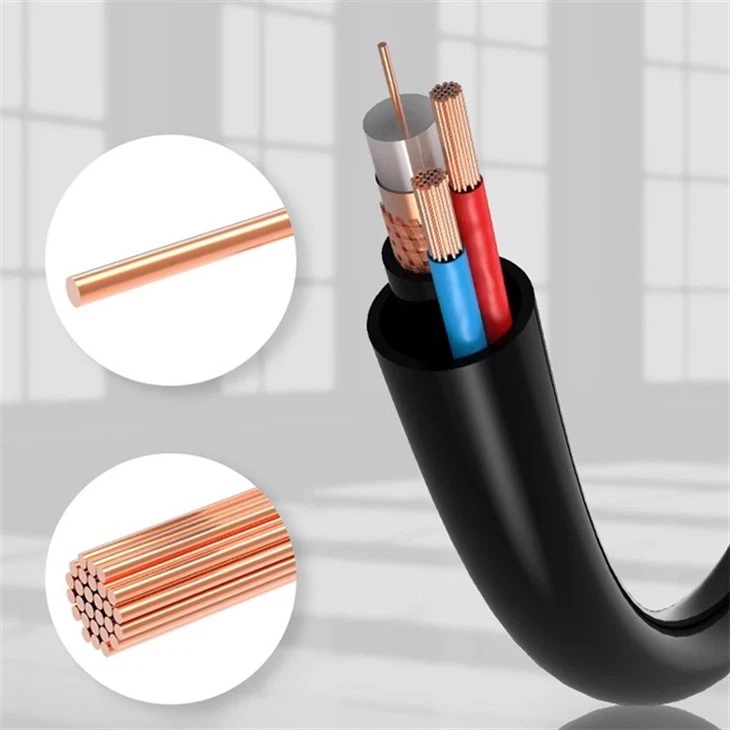


Handle With Care
Always handle patch cords with care and avoid pulling or twisting them. Do not use excessive force to insert or remove them from sockets.
Check For Damages
Regularly inspect your patch cords for signs of wear and tear, such as cuts, frayed insulation, and loose connectors. Any such damage can cause signal loss and must be repaired or replaced immediately.
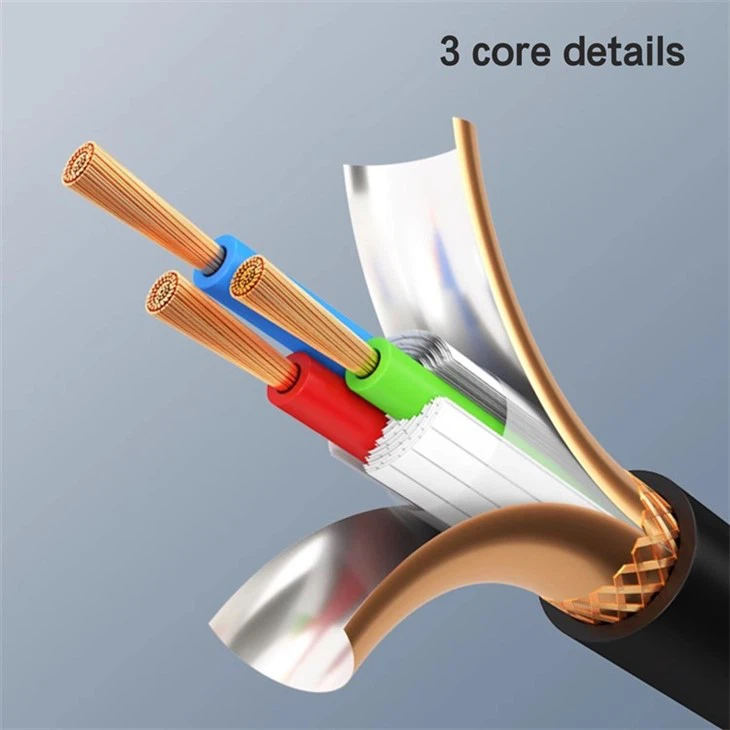

Test Regularly
Use a cable tester to check the integrity and continuity of your patch cords regularly. This will ensure optimum performance and help you identify any issues before they become a problem.
Certifications






Our Factory
Shenzhen Haikang Plastic Wire and Cable Co., Ltd. is a comprehensive trading company specializing in the production and processing of copper core cables and wires. The company has advanced production equipment, a strong technical team, and complete testing methods. With strong technical expertise, first-class equipment and perfect management system, it takes a leading position in innovative cable design and manufacturing. The company has its own factory in Chigang Town, Jieyang City, Guangdong Province, China, with a fifteen-year development history and rich production experience.

FAQ













