Common coaxial structures typically include SMA, BNC, etc., which are well-known due to their widespread use. However, the coaxial series is not limited to these few interfaces; in various applications, coaxial can be said to have a particularly rich array of interfaces. In this issue, we will take a look at how many types of coaxial interfaces you are familiar with, in a guessing game format.
SMA Operating frequency from 0 to 18GHz, SMA is a widely used small-sized threaded coaxial connector with superior performance and high reliability, extensively used in microwave devices and digital communication equipment for RF back to coaxial cable assemblies or microstrip lines.

SMB SMB, a push-in connector with a locking mechanism, is small in size, convenient for plugging and unplugging, has good vibration resistance, occupies little space, and is widely used in communication equipment, instruments, and navigation systems operating from 0 to 4GHz.

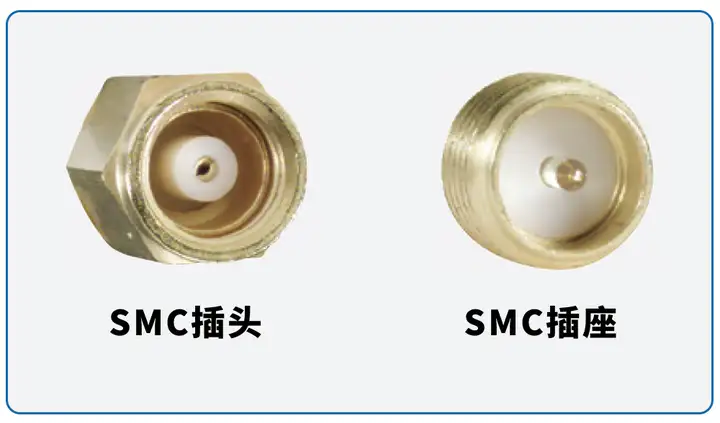
SMC SMC is a threaded variation of SMB, with internal structural dimensions identical to SMB, operating frequency from 0 to 11GHz, commonly used in radar, navigation, and more.

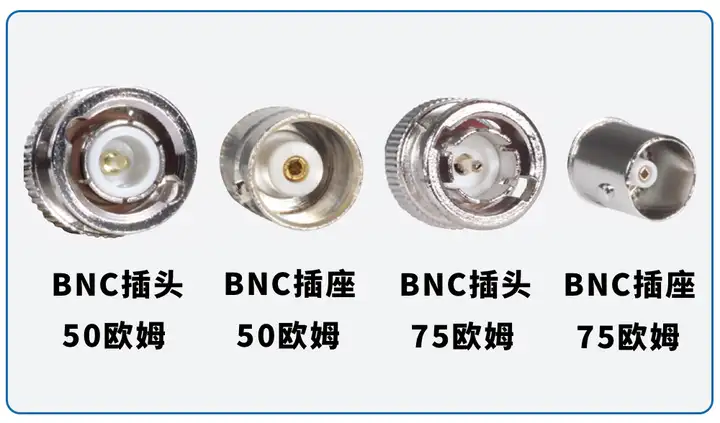
BNC With an operating frequency from 0 to 4GHz, BNC's main feature is its ease of connection, typically requiring less than a full turn of the connecting sleeve to connect. It is suitable for situations that require frequent connections and disconnections and is a widely used product, especially in the fields of instrumentation, networking, and computers.

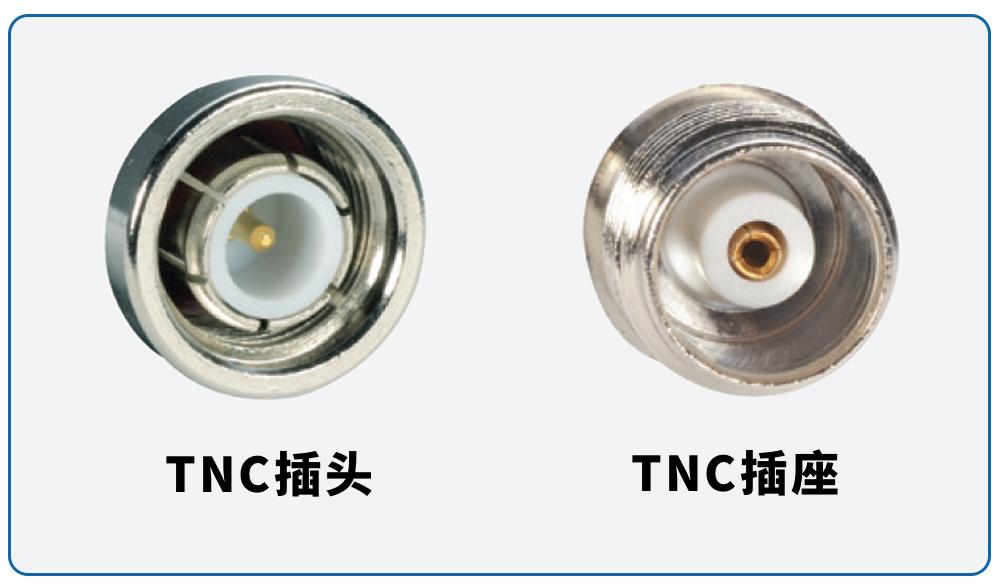
TNC TNC is a threaded variation of BNC, also known as threaded BNC, with an operating frequency up to 11GHz and good vibration resistance.

RCA Commonly known as the phono socket, RCA uses coaxial transmission of signals, with the central axis transmitting the signal and the outer ring contact layer grounding. Applications include analog video, analog audio, digital audio, and component color difference transmission.

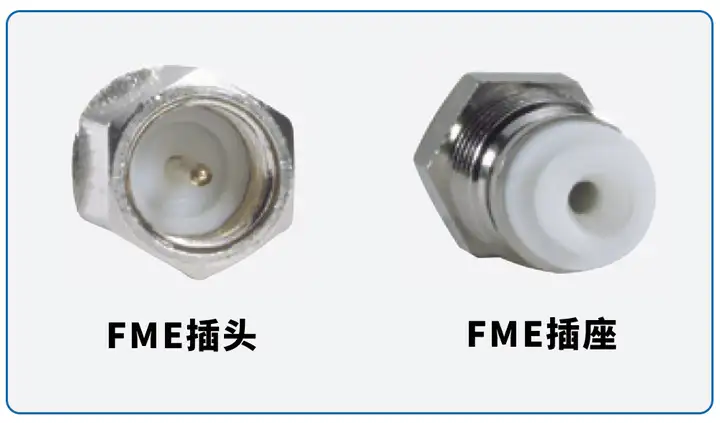
FME Also a compact small-sized coaxial interface, commonly used in vehicle-mounted equipment because the cable socket structure is also very small, installation is very simple, does not occupy much space, and can be easily converted to other types of connectors.

F-type The F series coaxial connector is a medium-small sized threaded connector, mostly used in video transmission networks and public antenna systems.

MMCX A new type of push-in connector, it is currently the smallest connector in use.
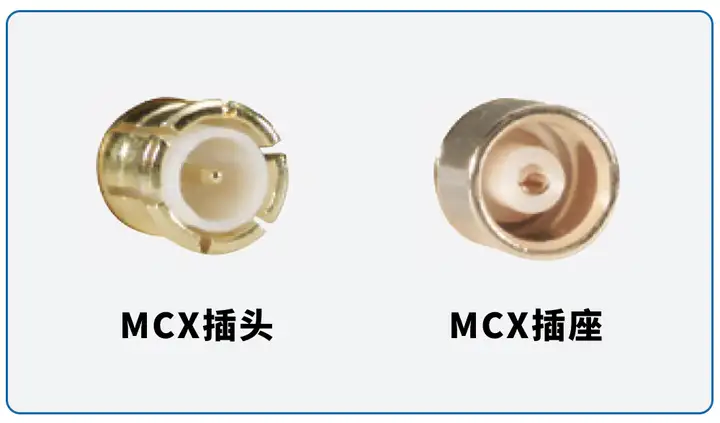

MCX Its basic function is similar to SMB, but it is one-third smaller in size.

N-type The N series uses threaded interconnection, available in 50 and 75-ohm versions. Operating frequency from 0 to 11GHz, it can be matched with 3 to 12mm soft, semi-flexible, and semi-rigid cables. Precision N connectors are even used in environments up to 18GHz, typically in local area networks, testing equipment, satellites, etc.
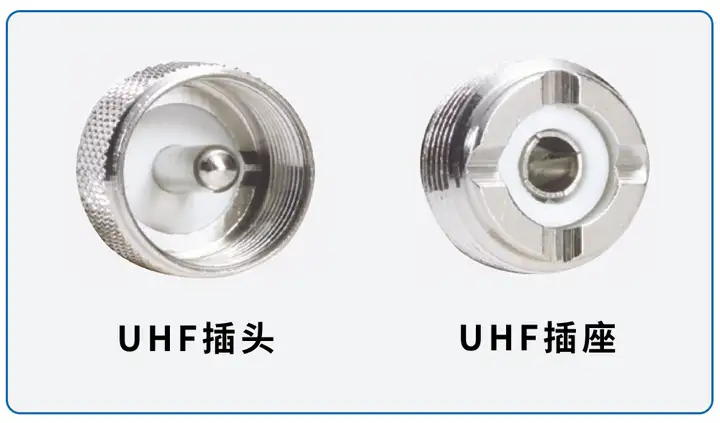

UHF Similar to most other coaxial connectors in terms of wiring, UHF connectors come in soldered and crimped types. The soldered type involves soldering the central conductor and the cable shield. The crimped type involves crimping the central conductor and the cable shield, which is efficient and performs well. The soldered type is stable and reliable. Generally, flexible cables use the crimped type, while semi-flexible and semi-rigid cables use the soldered type.

QMA QMA and QN connectors are both quick-connect connectors, with two main advantages: one is the ability to connect quickly, far faster than connecting a pair of SMA connectors; the other is that quick-connect connectors are suitable for connections in tight spaces.

TRB This series of interfaces features quick plugging and unplugging, stable electrical performance, and is used for data transmission occasions requiring higher shielding performance.

NMO The NMO type connector is one of the commonly used RF connectors on mobile-mounted antennas, especially when installed on the roof of a vehicle or on the top of an outdoor control box, these coaxial connectors come in handy.
↓ The following types of coaxial connectors correspond to specific brands.
Tips: Classification of Coaxial Connectors
When we look at coaxial connectors, the most obvious difference in appearance is size. Here's a summary to make classification easier:

Standard Size Includes N series, C series.
Small Size Includes BNC series, TNC series.
Ultra-Small Size Includes SMA, SMB, SMC, MCX, BMA, and SAA series.
Micro Size Includes SSMA, SSMB, and MMCX series.
Note: There are several types of coaxial connectors not introduced in the first part, which are briefly introduced here.
C Series Successfully developed by Concel, it uses an internal snap-on connection method, with internal nominal dimensions and operating frequencies the same as the N series, but not as universally used as the N series.
BMA Series Also known as blind mate connectors, their fixed sockets have a certain amount of axial and radial play, allowing for block-style, modular system assembly, quick blind replacement, and operating frequency from 0 to 22GHz. Internal nominal dimensions and compatible cables are the same as SMA.
SAA Series A push-in self-locking connector is currently widely used in programmable switches, optical terminals, and other communication systems.
SSMA Series Structurally similar to SMA but smaller in size, operating frequency can reach up to 40GHz, currently a standard millimeter-wave connector.
SSMB Series is Structurally similar to SMB but more compact.

