PoE (Power over Ethernet) is known as Ethernet power supply. Simply put, it can provide both power and data transmission through a single network cable for PoE-supported powered devices (PD).

The powered devices mentioned here include wireless access points (AP), IP cameras, other powered switches, etc. These devices connect with PoE switches to obtain power and transmit data. What are the advantages of using PoE? Easy Installation PoE is not limited by fixed power outlets and can be easily set up even in houses with old electrical infrastructure.
Simplified Wiring, Reduced Installation and Maintenance Costs Devices powered by PoE, since they only need one network cable to complete both power supply and data transmission, can avoid the connection of too many power adapters and cables.
It also helps reduce the installation and daily operational costs of infrastructure because it can utilize existing network infrastructure, allowing for easy deployment and centralized management of power output through switches to save costs.
Safe and Reliable Active PoE has a "handshake" test before device connection to confirm compatibility between devices (the specific principle is mentioned at the end of the article).
Moreover, in the event of power outages, PoE technology can also provide reliability assurance. For example, security cameras and access control systems powered by PoE in modernized computer rooms equipped with uninterrupted power supply systems will not lose security protection due to power interruptions. What are the standards for PoE? There are many standards and protocols for PoE, some are proprietary standards of manufacturers, some are industry standards approved by IEEE, and some even use network cables as a medium to transmit electrical power and analog signals.
The common PoE standards generally include the following three:
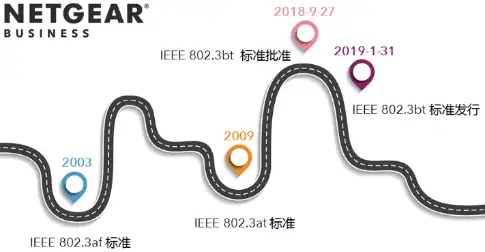
PoE Standard Protocol number IEEE 802.3af, which is the original PoE standard6. It outputs 15.4W of power from the Ethernet port, with an output power of 12.95W at 100 meters from the switch.
PoE+ Standard Protocol number IEEE 802.3at, PoE+ doubles the output power of the Ethernet port. It can provide 30W of power output, with an output power of 25.5W at 100 meters from the switch.
PoE++ Standard Also known as Ultra PoE, UPoE (abbreviation for Ultra PoE, different from Universal PoE's UPoE, which is a proprietary protocol), or 4PPoE.
Although the names are different, they all refer to the recently approved PoE protocol IEEE 802.3bt. This standard provides 60W to 90W of power output per port. Under the 60W standard, the output power is 51W at 100M from the switch. PoE Power Transmission Modes PoE usually uses three modes to transmit direct current power through Ethernet cables, namely:
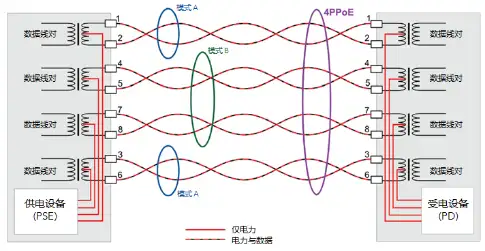
Mode B, also known as Alternative B or Alt B, sometimes called Mode B;
Mode A, also known as Alternative A or Alt-A, sometimes called mode A;
A mode used in the 802.3bt protocol is 4PPoE, which is why some people use the keyword 4PPoE to refer to the PoE++ protocol. Mode B For 100 BASE-T Fast Ethernet, data transmission uses 2 of the 4 pairs of twisted-pair cores, namely pins 1, 2, 3, and 6. PoE's mode B uses the idle 2 pairs, or 4 cores, for power transmission, namely pins 4, 5, 7, and 8. This is easy to understand, but it does not mean that power delivery on 100 BASE-T Fast Ethernet must use mode B.
Mode A Mode A uses pins 1,2,3,6 for power transmission, meaning that for Fast Ethernet as well as for higher-speed networks of 1G/2.5G/5G/10Gbps, power and data are transmitted through the same c.
4PPoE 4PPoE stands for "4 Pair transmission PoE," and this mode is adopted by the 802.3bt protocol, which uses all 4 pairs or 8 cores of the twisted pair for power delivery.
Which power transmission mode to choose? The power-supplying device decides which power transmission mode to use (Alt A, Alt B, or 4PPoE), and the powered device needs to support all the power transmission modes it should support.
For example, a device compliant with IEEE 802.3at can support both mode A and mode B; a device compliant with IEEE 802.3bt also needs to support the 4PPoE mode.