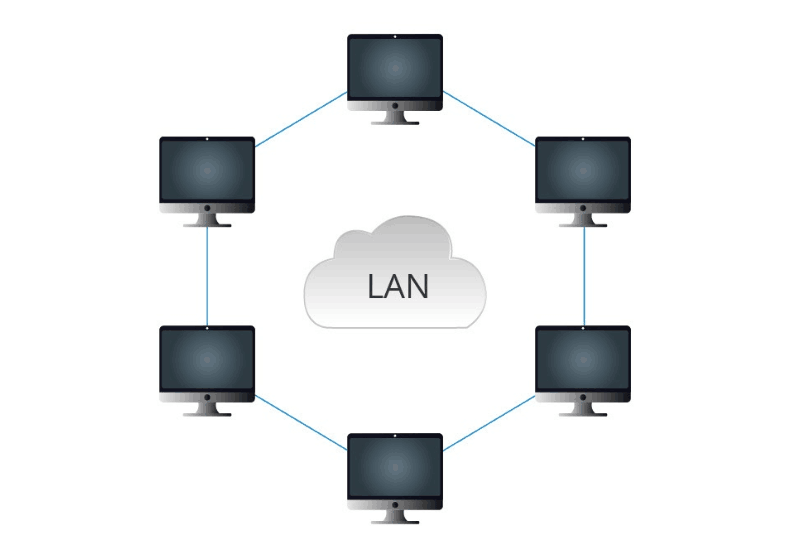
What is LAN? LAN (Local Area Network) is the most common and widely used type of network. It refers to a computer network that achieves resource sharing by connecting two or more computer devices (such as servers, workstations) within a range of 1-5 kilometers through cables (such as coaxial cables, twisted pair cables, optical cables, etc.), such as homes, offices, schools, or building groups with computers, servers, and peripheral devices (such as printers, scanners, projectors, and other storage). At present, Ethernet (IEEE 802.3 standard) is the most common way of networking in local area networks. In recent years, with the establishment of the 802.11 standard, wireless protocols such as IEEE802.11a/b/g/n have been widely used, and the application of wireless local area networks is becoming more and more popular. In addition, the types of LAN (Local Area Network) also include token ring and FDDI (Fiber Distributed Data Interface, IEEE 802.8).
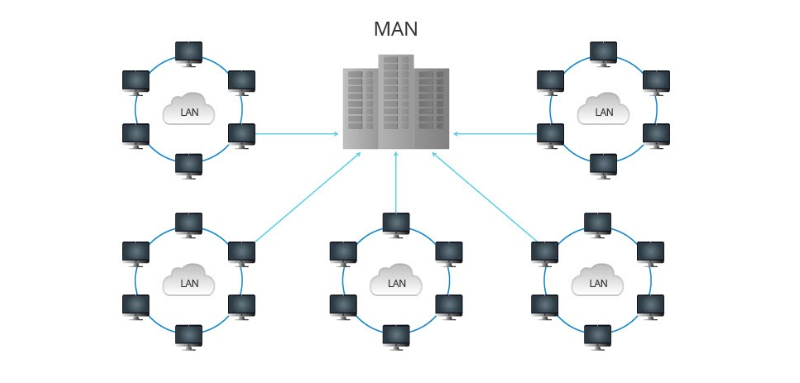
What is MAN? MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) refers to a computer network established within the same city, which can cover up to sixty kilometers. The transmission delay of the MAN is small and the speed is fast. It can be used as a backbone network, connecting hosts, databases, and LANs at different locations in the same city through optical cables to establish a high-speed connection network. Common protocols for MAN include Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), Distributed Queue Dual Bus (DQDB), and Switched Multi-megabit Data Service (SMDS), etc.
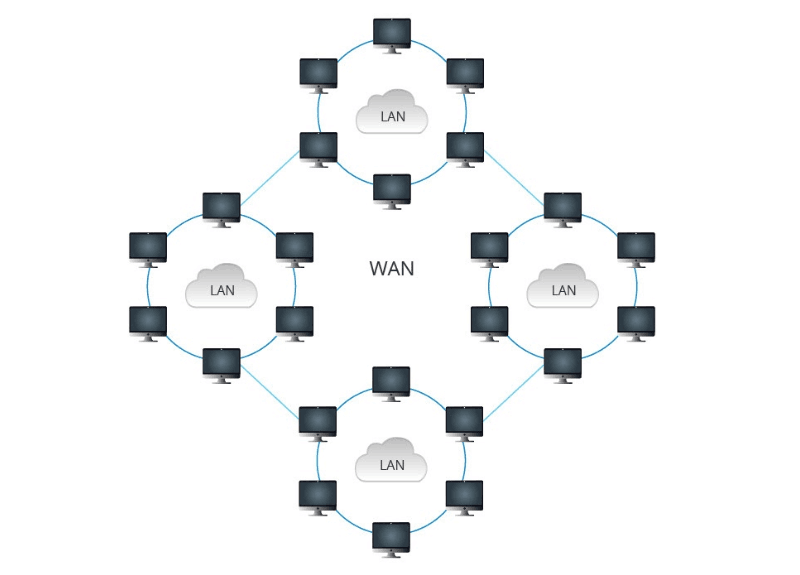
What is WAN? WAN (Wide Area Network) refers to a computer network that connects different regional LANs or MANs. Its coverage is wide, covering thousands of kilometers, and can connect multiple regions, cities, and countries, even spanning several continents to achieve long-distance communication. Compared with LAN (Local Area Network) and MAN (Metropolitan Area Network), WAN (Wide Area Network) involves more diverse devices, such as routers, switches, firewalls, etc. The various branches of a company can establish WAN connections for communication through microwaves, satellite channels, etc. Currently, commonly used protocols for WAN (Wide Area Network) include Frame Relay, Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), High-Level Data Link Control Protocol (HDLC), and Synchronous Data Link Control Protocol (SDLC).
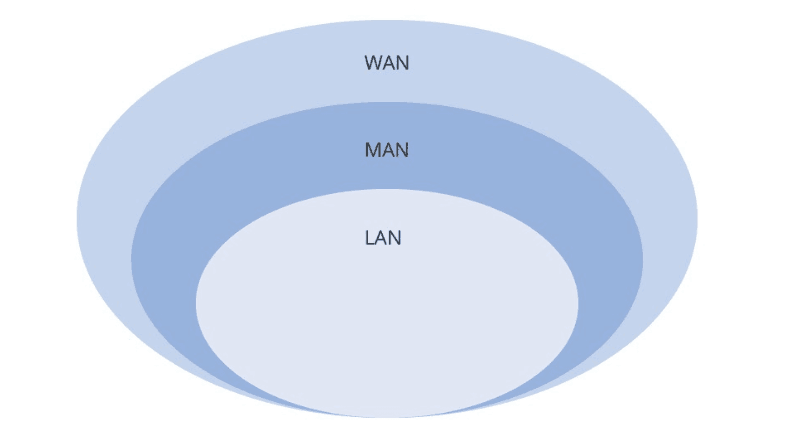
What is the difference between LAN, MAN, and WAN? As we know, LAN, MAN, and WAN are all types of computer networks. Although the nature of communication is the same, these three types of networks still have differences in terms of coverage and application. The differences between LAN, MAN, and WAN are as follows:
1.Coverage As mentioned above, the coverage of the three networks from small to large is LAN (Local Area Network), MAN (Metropolitan Area Network), and WAN (Wide Area Network).
2.Transmission Medium Usually, LAN (Local Area Network) uses wireless WiFi or 100/1000Mbps network cables for communication; MAN uses 100Mbps optical cables or modems; while WAN, unlike communication between users, generally uses telephone lines, high-speed data lines, satellites, microwaves, etc. for communication, its transmission rate is lower compared to LAN (Local Area Network).
3.Application The establishment of a LAN (Local Area Network) can effectively reject access from illegal users, ensuring the security of the business, and is suitable for corporate intranets. For MAN (Metropolitan Area Network), the most common is the cable television network in every household in each city. In addition, various government agencies or enterprises can also rely on MAN to connect offices in different regions. For services like military services, railway reservations, airlines, etc., which have high requirements for network security, high-security communication can be achieved by establishing a WAN (Wide Area Network).
4.Setup and Maintenance Due to the fewer network nodes in the LAN (Local Area Network), it is easier to establish and maintain compared to the MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) and WAN (Wide Area Network).
| Parameter | LAN (Local Area Network) | MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) | WAN (Wide Area Network) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network Ownership | Private | Private or Public | Private or Public |
| Coverage | Small | Medium | Large |
| Setup and Maintenance | Easy | Difficult | Difficult |
| Bandwidth | Low | Medium | High |
| Speed | High | Medium | Low |
| Network Congestion | Less | More | More |
| Applications | Schools, Hospitals | Towns, Cities | Countries, Continents |
Summary After the above introduction, I believe you have a more detailed understanding of the three types of computer networks: LAN/MAN/WAN, and clearly know their applications in different fields and their significance, so as to make a more correct choice for network deployment.

